


近日,我校资源与环境学院土壤生物化学与环境课题组黄巧云团队在微生物重金属抗性基因高通量检测方面取得重要进展,相关成果以“MRG Chip: A High-Throughput qPCR-Based Tool for Assessment of the Heavy Metal(loid) Resistome”为题发表在Environmental Science & Technology。
重金属抗性机制在帮助微生物抵抗重金属毒性的同时,也驱动了金属的生物地球化学循环。由于环境微生物重金属抗性基因复杂多样,在微生物群落水平对多种重金属抗性基因进行定量分析难度较大。本研究基于高通量qPCR技术开发了一种重金属抗性基因芯片(MRG Chip),用于微生物重金属核心抗性组研究。MRG芯片可对9种重金属(铜、银、汞、铬、锌、铅、镉、钴、镍)的56个抗性基因进行高通量定量检测,具有高效、快速、准确、灵敏度高、特异性强、覆盖范围广等特点。MRG芯片共覆盖29门382属的微生物类群,>94%的引物扩增效率为80-110%,可在3小时内完成54个样品的重金属抗性组定量分析,目前已成功运用在土壤、沉积物、灰尘、粪便等环境样品重金属抗性组的检测。MRG芯片的研发为表征环境微生物重金属抗性组提供了有利的高通量检测手段,未来有望在重金属抗性组特征及环境驱动因素等相关研究中发挥重要作用。
资源与环境学院博士研究生朱姣姣为论文第一作者,郝秀丽副教授为通讯作者。云顶yd222备用线路检测黄巧云教授、陈雯丽教授、蔡鹏教授、刘玉荣教授、罗雪松副教授、中国科学院城市环境研究所苏建强研究员、福建农林大学Christopher Rensing教授、中国地质大学赵忆副教授也参与了该项研究。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金、国家重点研发计划和中央高校基本科研专项基金资助。研究团队已为该芯片及其应用申请了发明专利。
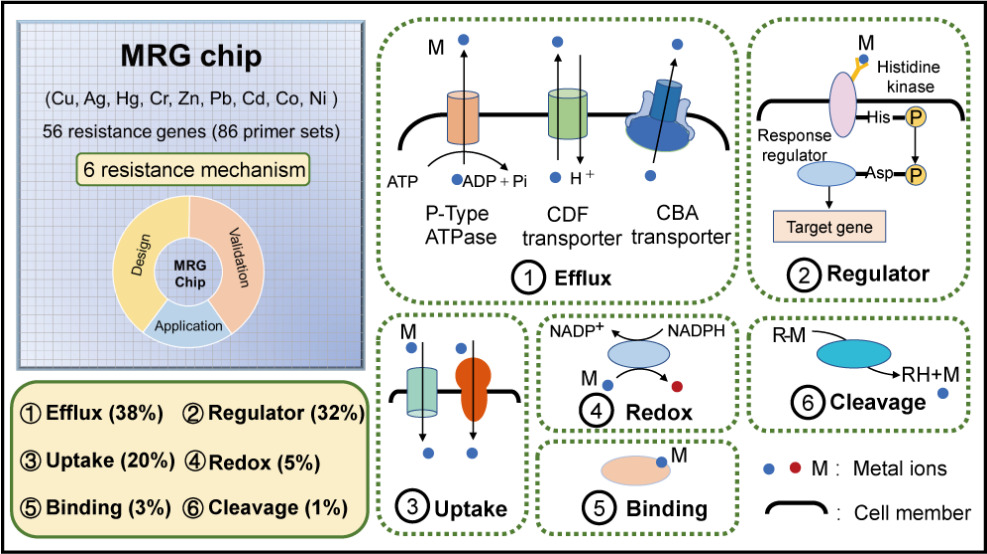
重金属抗性基因芯片示意图
南湖新闻网讯
通讯员:朱姣姣
审核人:郝秀丽
【英文摘要】
Bacterial metal detoxification mechanisms have been well studied for centuries in pure culture systems. However, profiling metal resistance determinants at the community level is still a challenge due to the lack of comprehensive and reliable quantification tools. Here, a novel high-throughput quantitative polymerase chain reaction (HT-qPCR) chip, termed the metal resistance gene (MRG) chip, has been developed for the quantification of genes involved in the homeostasis of 9 metals. The MRG chip contains 77 newly designed degenerate primer sets and 9 published primer sets covering 56 metal resistance genes. Computational evaluation of the taxonomic coverage indicated that the MRG chip had a broad coverage matching 2 kingdoms, 29 phyla, 64 classes, 130 orders, 226 families, and 382 genera. Temperature gradient PCR and HT-qPCR verified that 57 °C was the optimal annealing temperature, with amplification efficiencies of over 94% primer sets achieving 80–110%, with R2 > 0.993. Both computational evaluation and the melting curve analysis of HT-qPCR validated a high specificity. The MRG chip has been successfully applied to characterize the distribution of diverse metal resistance determinants in natural and human-related environments, confirming its wide scope of application. Collectively, the MRG chip is a powerful and efficient high-throughput quantification tool for exploring the microbial metal resistome.